Hey guys, today we wanted to share a post with you about reading nutritional labels at the supermarket.
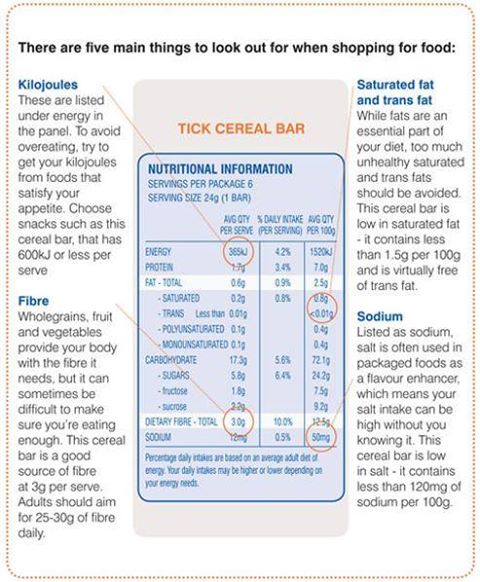
This photo depicts a nutritional information panel that may be found on any foods in the supermarket, but in this case, its on a cereal bar. The panel that says ‘avg qty per serve’ shows the amount of each of the macronutrients in that particular food. You should look for snacks that contain less than 600kJ per serve. This is the energy content of the food and how much it will contribute to your daily total.
Next is the protein content. Some protein is better than none, and the protein content may be higher in snack foods containing nuts, dairy or meats (where possible).
When reading the fat section it’s important to focus on the saturated and trans fats. You want to limit your intake of saturated fats and try to avoid trans fats where possible. For fats it’s important to look at the ‘per 100g’ panel. Try to choose snacks or foods that contain less than 1.5g per 100g of saturated fat.
As far as carbohydrates go, it’s important to look at the ‘sugar’ section under the main heading. Some snack foods will naturally have sugar if it contains fruits or milks for example (fructose & lactose), but it is important to distinguish this from sucrose/sugar that may be added to enhance flavour. It’s best to look at the ingredient list directly and see if cane sugar/sugar are listed as one of the first ingredients. If it is, it may be wise to choose another option. That being said, it is nearly impossible to avoid all added sugars unless you really endeavour to do so. It would be preferable if ‘sugar’ didn’t account for 50% of the total carbohydrate amount.
For sodium (salt) it’s important to look for foods with less than 120mg per 100g. Foods shouldn’t be loaded with extra salt, but usually it’s added as a flavour enhancer, so be careful!
All this being said, you don’t have to meticulously check every single food label! It’s more about being aware of what foods you are choosing at the supermarket and what you are putting in your body! Make every choice count, but don’t be afraid to include treats as part of a healthy and balanced diet.
Mission Nutrition 🙂